A new Nissan-led project aims to build UK R&D capability and strengthen technical expertise around zero emission vehicles and batteries.
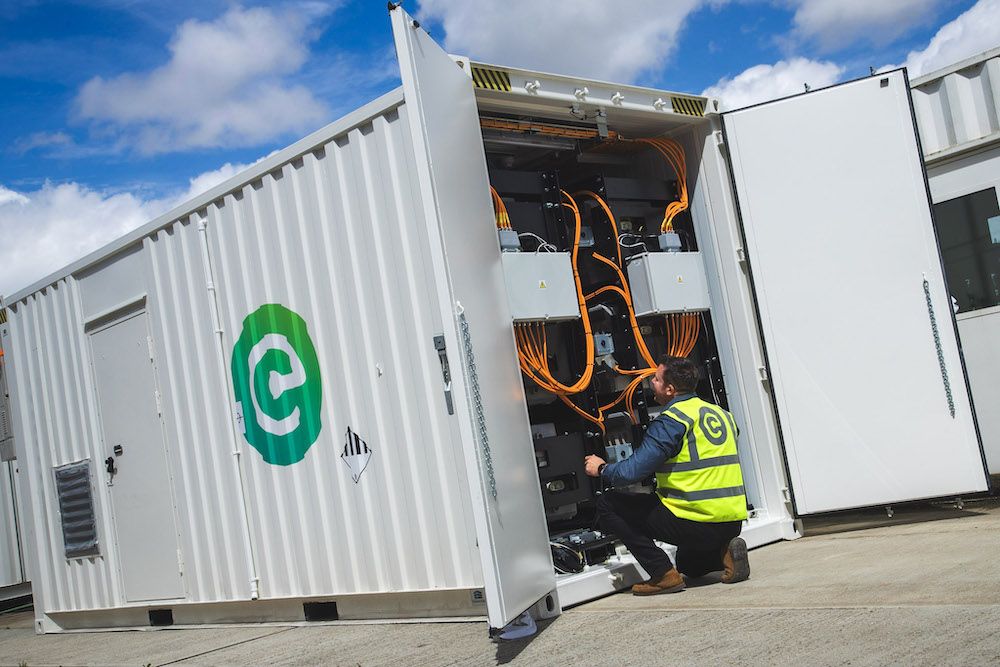
Connected Energy will lead on the second-life battery element of the project, building on its existing technology to deliver large-scale energy storage sites using EV batteries.
The project will develop energy storage technology which uses multiple battery types with different states of health and performance characteristics.
This will enable the company to demonstrate the ability of large scale second life systems to compete with new lithium-ion systems.
At present, Connected Energy produces 300-kilowatt systems designed for smaller-scale industrial and commercial applications. This project is key to its strategy to scale-up its technology.
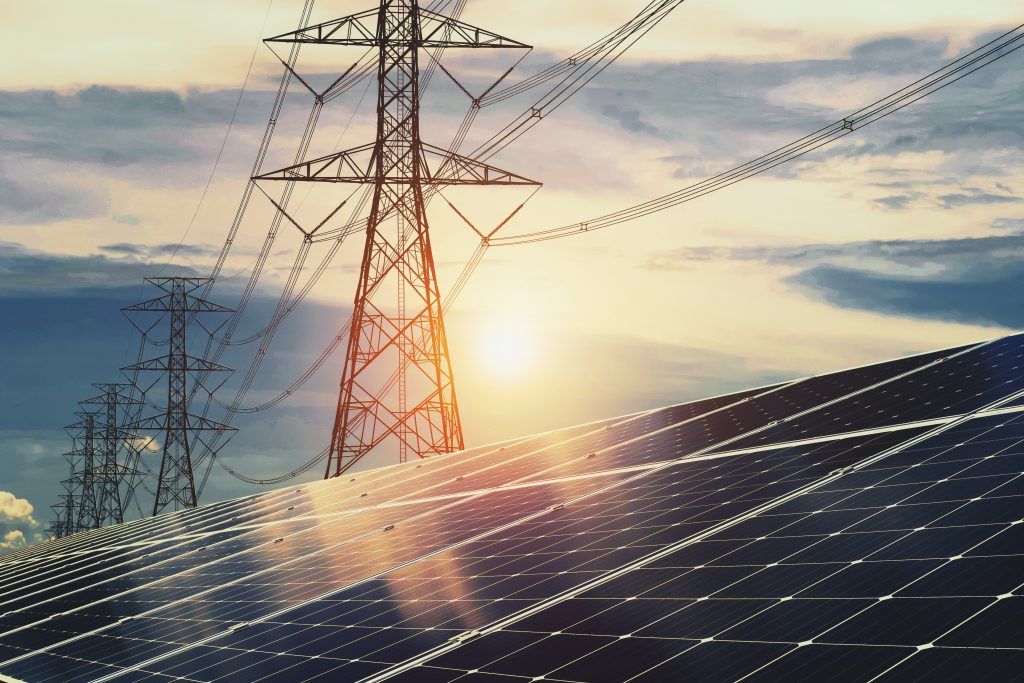
Large-scale battery energy storage systems can be used to support the energy flexibility and demand markets, storing energy when it is in abundance and selling it back to the grid when demand and prices are higher.
The multi-megawatt system to be deployed by Connected Energy will become operational in 2025. It is part of a wider £30.1 million consortium project, which includes £15m of Advanced Propulsion Centre UK (APC) funding and aims to strengthen the UK’s capabilities in EV battery reuse, recycling and grid balancing.
The overall consortium is led by Nissan and partners also include lithium battery recycling experts Altilium, alongside Connected Energy.
Matthew Lumsden, CEO of Connected Energy, said:
“Our goal is to develop and demonstrate a pioneering economic model for large-scale second life energy storage systems that can be easily scaled up further and replicated.
“This will place Connected Energy and our network of partners at the leading edge of second life battery use. Repurposing EV batteries in energy storage is a key contributor to vehicle electrification and sustainability while also helping towards the decarbonisation of the electricity grid.”
Image courtesy of Connected Energy